Last updated on November 25th, 2023 at 02:22 am
This post may contains affiliate links which means I may receive a commission from purchases made through links. Learn more from affiliate policy page.
Table of Contents
Do you wish to know what is the difference between AC and DC Power? Yes, The amount of power consumed by a home alarm system may fluctuate depending on factors such as the type of system, its design, and battery usage.
Have we all known what Covid 19 have done to our economy? For the past few months, I have been getting crazy bills for electricity.
Through their journey of finding the most ideal home alarm system, they realized the impact of power usage on their monthly bills and the environment.
Let me show you how to find out and explore the power consumption of some home alarm systems and their examined components, like control panels, sensors, and connectivity devices.
Gain insights into power usage patterns and efficiency optimization strategies.
Let’s dive in together.
An alarm system can refer to different types of alarms, for example, burglars or home security.
Here is what the search results say about the electricity usage of different types of alarms:
1. Burglar alarms: On average, a burglar alarm always left on will use about 0.168 kWh daily. Over the year, this will build up to around 61.32 kWh, resulting in an annual cost of approximately $22.70.
According to another source, the amount of power a burglar alarm consumes is minimal and hardly worth discussing. However, the power usage increases when the notice is in use.
2. Home security alarms: Home security alarms are low voltage systems that are not wired directly into the house power but are powered from the wall
A home security alarm’s power usage resembles a Burglar Alarm’s.
3. Alarm clock radios: Modern alarm clocks with built-in radios that are Energy Star-rated use between 1 and 2 watts of power. At the same time, some older models or models with several features are available.
4. Ring Alarm Base Station: According to measurements, the Ring Alarm Base Station consumes anywhere from 12.4 to 24 watts of power.
Comparing Factors of AC and DC Power
While AC provides the bulk of electricity transmitted from power plants, DC runs many consumer devices. Their distinct attributes suit them to play these different roles.
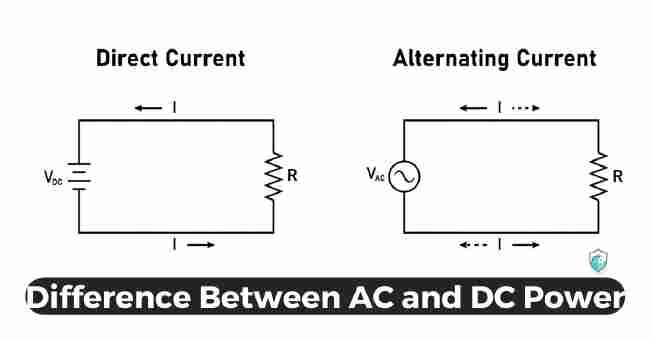
Here’s an overview comparing factors between alternating and direct current electricity:
| Factor | AC | DC |
|---|---|---|
| Flow | Periodically reverses direction | Unidirectional flow |
| Voltage | Varies sinusoidally between positive/negative peaks | Stays constant |
| Frequency | Rate (Hz) of sinusoidal oscillations per second | No frequency |
| Transmission | Highly efficient even over long distances | Significant losses over distances |
| Generator | Uses electromagnetic induction | Variable methods (PV, turbine, battery) |
| Common Uses | Power grids, motors, appliances | Electronics, batteries, vehicles |
Below we’ll clarify these contrasts and why they matter. Gaining this context helps appreciate why AC or DC gets utilized for different applications.
AC vs DC Flow Direction
The alternating versus direct flow remains the most fundamental difference. With AC electrons periodically reverse course. They flow forward, then backward – mimicking an oscillating wave.
DC instead features a continuous unidirectional current. Electrons always flow smoothly in a single direction between power points.
This core electron direction distinction impacts all other AC/DC characteristics. Cyclical current reversals enable AC to induce electromagnetic fields in transformer coils.
This allows easy voltage conversion – a key advantage in power distribution we’ll revisit later.
AC vs DC Voltage Characteristics
Beyond flow direction the voltage itself acts differently. With AC power, voltage perpetually undulates following the alternating current.
So an AC circuit’s voltage constantly crosses between positive and negative peaks. At certain moments it equals 0 when transitioning polarity.
A DC circuit maintains a steady, non-fluctuating level. Like a car cruising at a constant 60 mph, DC voltage remains fixed unless manually adjusted.
This stability suits sensitive electronics requiring smooth predictable power.
Ac Voltage Frequency
Given AC’s back-and-forth current shifts, we can measure cycles per unit time. Frequency defines an AC signal’s oscillation rate, quantified in Hertz (Hz).
Most countries standardize devices and household power to operate at either 50 or 60 Hz.
As AC voltage swings positive then negative, one full cycle completes in 1/60th of a second (for 60 Hz power). Frequency directly correlates to wavelength – the peak-to-peak duration of each AC cycle:
DC lacks this frequency concept. With no periodic oscillations, Hz becomes meaningless for direct current circuits.
Why AC Frequency Matters
Frequency compatibility is vital where AC electricity gets used. Motors and appliances must run at design specifications to function properly. Deviations risk damage.
That’s why power grids maintain consistent AC frequency and households access standardized wall sockets. Any devices you plug in rely on stable 60 Hz (or 50 Hz) power to operate safely.
Transmitting AC vs DC Over Distance
A major benefit of AC comes transmitting it across vast distances. High voltage AC can move extremely efficiently over hundreds of miles with marginal energy losses.
This enables economical distribution from distant generating stations to populous cities.
Direct current doesn’t transmit as effectively. At high voltages DC cables dissipate more energy as heat, requiring thicker wires. Historically this made DC unsuitable for interconnected grids.
However modern advancements are lowering long-distance DC transmission costs – an active area of electricity research.
HVDC lines now relay electricity between distant AC grids with improved efficiency.
Why Electronics Run on DC Power
Though AC dominates utility transmission, most consumer electronics require smooth direct current.
Sensitive solid-state components like integrated circuits rely on stable voltage without periodic polarity changes.
That’s why devices like phones, computers and LED lights utilize AC/DC converters.
Embedded circuits rectify household AC into the steady low-voltage DC that electronic components need.
Batteries also supply DC electricity to power portable electronics. Chemical reactions between battery terminals generate reliable DC current able to smoothly energize mobile devices.
FAQs
What Factors Affect The Power Usage Of A Home Alarm System?
Several factors can affect the power usage of a home alarm system.
Here are some factors that can affect the power usage of a home alarm system:
Type of Alarm System: The different alarm systems may have other power usage. For example, a Burglar Alarms system requires around 7-8 watts of power, while a house alarm can’t use more than a few watts.
Age and model of the Alarm System: Newer models of Alarm Systems are generally more energy-efficient than older models.
Were you aware that contemporary alarm clocks that have radios are Energy Star-certified and consume only 1 to 2 watts of power? However, older models with added features may consume more energy.
Frequency of occupancy: The frequency of your home’s occupancy can affect the power usage of your alarm system.
If you are away from home for extended periods, your alarm system may use less power.
Alarm monitoring service: Whether or not you have an alarm monitoring service can affect the power usage of your alarm system.
If you have a monitoring service, your alarm system may use more power to transmit signals to the monitoring centre.
Power source: Most alarm systems on the market use a 12-volt battery resembling a miniature car battery with the 1875 terminals, often known as “F1”.
The power usage of an alarm system is not directly related to the power source.
Overall, the power usage of a home alarm system is relatively low, and there will be no significant impact on your electricity bill.
How Does The Frequency Of Alarm Activation Affect Power Usage?
The frequency of alarm activation can affect the power usage of a home alarm system.
However, the search results do not directly answer this question. Here is what the search results say about the relationship between occupancy and power usage:
Occupancy: Some factors affecting energy usage include the frequency of your home’s occupancy.
Occupancy schedules and density one’s influence can have a significant impact on building plug, lighting, and air conditioning energy usage.
Ultrasonic sensors use the Doppler principle to detect occupancy by emitting an ultrasonic high-frequency there is a signal issue throughout the area space.
Alarm system power usage: A house alarm can’t use more than a few watts. It is likely to use a maximum of a few quid at most.
A burglar alarm generally requires around 7-8 watts of power to run normally and will use about 60-70 kWh of electricity annually.
How Can I Reduce The Power Consumption Of My Home Alarm System?
Here are some ways to reduce the power consumption of your home alarm system:
Upgrade To Energy-Efficient Models: Modern alarm systems generally show a higher tendency towards energy-efficient than older models.
Energy Star-rated alarm clocks with built-in radios use between 1 and 2 watts of power, while some older models or models with few extra features may use more.
Consider upgrading to an energy-efficient model to reduce power consumption.
Use Detectors Equipped With Leds: Detectors equipped with LEDs in communication routes can turn on automatically when necessary, minimizing unnecessary power consumption at night.
Turn off the Alarm System when Unnecessary: If you are going to be away from home for an extended If you experience menstrual cramps, consider turning to some remedies to relieve the alarm system to reduce power consumption.
Disconnect the Alarm System Box from the Outlet: If the power is out and you need to turn off the alarm system, disconnect the package from the outlet by unplugging it.
Please remove the battery from the box to ensure it does not continue To use electricity.
Use a 12-volt Battery: Many of the alarm systems available today operate on a 12-volt battery that looks like a smaller version of a car battery. These batteries are commonly referred to as having “F1” terminals, which measure .1875 inches.
Ensure that your alarm system uses a 12-volt battery to minimize power consumption.
How Many Volts Does An Alarm System Use?
Here is what the search results say about the voltage used by home alarm systems:
Power source: Most alarm systems on the market use a 12-volt battery resembling a miniature car battery with .1875 terminals, generally called an “F1”.
Voltage range: The actual voltage on an alarm system loop doesn’t matter; The voltage range can vary from 1.5 to 20 volts. Depending on the manufacturer.
The voltage at the detector should be a stable reading of approximately 13 to 13.6V.
It is widely believed that home security systems are a safe option, thanks to their use of low-voltage equipment.
Low-voltage circuits benefit pre-wiring alarm systems because they use less current than standard wiring.
Overall, the voltage used by a home alarm system is relatively low and should not pose a danger to homeowners. Most alarm systems on the market use 12-volt batteries as their power source.
What Is The Typical Power Consumption Of A Home Alarm System?
The typical power consumption of a home alarm system can vary depending on the type of alarm system.
Here is what the search results say about the power consumption of different kinds of home alarm systems:
Alarm Clock Radios: A standard Alarm clock radio using 2 watts for 24 hours daily will cost around $0.10 per kWh.
House Alarms: A house alarm can’t use more than a few watts. It is likely to use a maximum of a few quid at most.
Burglar Alarms: On average, a burglar alarm requires around 7-8 watts of power and will use approximately 60-70 kWh of electricity per year.
One study found that ten home security systems had an average power consumption of 8.2 W (70 kWh/year).
Ring Alarm Base Station: The power usage of the Ring Alarm Base Station is between 12.4 watts and 24 watts.
Is An Alarm System AC or DC?
The power source for an alarm system is AC, but it uses a low-voltage transformer to charge a 12-volt backup battery.
Sometimes, the transformer can switch the AC input power from the outlet to the DC output power to the alarm panel.
Here is what the search results said on the Alarm System, whether it is AC or DC:
Power source: Most alarm systems on the market use a low-voltage transformer that charges a 12-volt backup battery.
The transformer is plugged into an AC outlet and transforms the high-voltage power into low-voltage power suitable for an alarm system.
Sometimes, the transformer may switch the AC input power from the outlet to the DC output power to the alarm panel.
Backup Battery: The backup battery for an alarm system works by slowly storing power while the panel is running on AC power.
During power outages, the system can function temporarily as the battery takes over to provide power.
The power source for an alarm system is AC, but it uses a low-voltage transformer to charge a 12-volt backup battery.
Sometimes, the transformer can switch the AC input power from the outlet to the DC output power to the alarm panel.
Can An Alarm System Run On Dc Power Only?
No, an alarm system cannot run on DC power only. It requires AC power from a plug-in transformer to operate, but Additionally, it possesses a backup battery that can provide energy in a power outage.
Most AC is necessary for the Alarm system’s power to operate, but a backup battery can provide power in a power outage. Please take note.
Here is what the search results say on an Alarm System that runs on DC power only:
Power Source: A security system receives AC power from a plug-in transformer. The transformer transforms the high-voltage power into low-voltage energy suitable for an alarm system.
It may involve switching the AC input power from the outlet to the DC output power to the alarm panel.
Backup Battery: Most alarm systems on the market use a 12-volt battery resembling a miniature car battery with .1875 terminals, mostly called an “F1”.
The backup battery is designed to keep a system running temporarily during AC loss situations.
The rechargeable backup battery will draw a small amount of power from the AC outlet to keep it charged.
Fire Alarm Control Panel: Fire alarm control panels have a DC power output that tells the operator that the panel’s DC power (batteries) is being charged or used.
While relying on DC backup power, The system is still experiencing issues.
What is the Difference Between AC and DC Power?
AC and DC power are two different types of current flow in a circuit. AC power alternates periodically between positive and negative voltage, while DC power flows steadily in a single direction.
These are the differences between AC and DC power:
AC Power:
- Alternates periodically between positive and negative voltage.
- The direction of the current periodically changes accordingly.
- One way to access electricity is through a generator or an outlet.
- They were used for long-distance power transmissions and power-hungry factories.
- AC power’s wave motions allow for efficient travel over long distances. This is due to power plants being able to generate significant amounts of AC power and which can be delivered through power lines with ease.
- The standard electricity that comes out of power outlets.
DC Power:
- The voltage is always constant, and the electricity flows in a specific direction.
- Flows steadily in a single direction.
- They are used to power electronics like phones, cameras, and computers.
- Far more consistent in terms of voltage delivery.
- Most electronics rely on it and use DC power sources such as batteries.
- It can be stored in batteries that use direct current.
- They are used in far-flung locations where AC power from electricity lines is not readily available.
- It cannot increase or decrease voltages as quickly as AC power.
Conclusion
Now that you have learned How Much Power Does A Home Alarm System Use?
It is essential to understand your system’s power needs, utilize energy-saving options, and perform routine maintenance to ensure consistent protection and performance.
By taking these actions, you can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your home alarm system while minimizing power consumption.
It’s important to keep in mind that a properly maintained alarm system with sufficient power not only brings peace of mind but also boosts the security of your home and family.
But I have an extensive article on Alarm system, click here to enjoy.

Comments are closed.